Many homeowners struggle to understand the various ratings given to windows and doors. A prospective buyer will typically look for perfect windows or doors that are excellent in all respects. Doors and windows are characterised using several metrics like looks, thermal efficiency or U-value, solar factors, etc. Doors are also classified based on single, double, or triple glazed glass used in them.
In this write-up, we’ll understand the concept of U-value, how it can help you make informed decisions and how it helps you save money in the long run.
What Does U-value Mean & How to Measure It?
U-values are used to measure how well different parts of a building conduct or move heat. You should know how to calculate the U-value of glasses. The U-value of a building is determined by measuring the rate of heat flow per unit area of the building and dividing it by the temperature differential on each side of the building. The number is given as W/m2K, which stands for watts per square metre per Kelvin (1°C = 1K).
A U-value of double glazing window of 1.4 means that for every degree of temperature change between the inside and outside of the window, 1.4 watts will be transferred per square metre.
When the U-value is high, there is more heat transfer, and when it is low, there is less heat transfer. This means that the building is better protected. When it comes to building parts like windows, the more energy-efficient a building is, the lower the U-value.
You can use U-values to measure the thermal efficiency of different parts of your home, such as:
- Walls
- Windows
- Doors
- Roof
- Floor
Common U-values Of Building Parts
Here are the average or common U-values of different parts of the home:
| Building Component | U-Value (W/m2K) |
| Insulated Wall | 0.18 |
| Solid Brick Wall | 2 |
| Solid Timber Door | 3 |
| Single Glazing | 4.8-5.8 |
| Double Glazing | 1.2-3.7 (depends on type) |
| Cavity wall with no insulation | 1.35 |
Window U-value Measurements: How Are They Different From Others?
When measuring windows’ U-value in comparison to other surfaces, there are some specifics that are different. These include:
- Ug Value = This gauges how well the glass conducts heat.
- Uf Value = Represents the window frame’s thermal efficiency.
- PSIG = Which represents the frame spacers’ thermal performance.
Some factors influence the U-value of windows:
- Type of glass you used (Low-e coated, standard float, laminated, etc.).
- The gas used between panes of glass (Argon, etc.).
- The space between the window panels
- Thermal characteristics of the spacer bar
- Components of the structure
- The number of glass panes utilised.
Why Are U-values Important To Consider?
Consumers can compare the energy efficiency of different products using the Window Energy Rating (WER). Rainbow stickers are easy-to-read ratings like those on fridges and washing machines.
WER rates use G-value in calculating ratings. Coated or triple glazed glass reduces light transmittance and lowers G-values by capturing less solar gain.
It is preferable to evaluate individual values independently for various purposes. In the United Kingdom, energy efficiency is primarily desired by minimising heat loss; therefore, the U-value is the most important value to consider.

How To Make Your Doors & Windows Energy-Efficient?
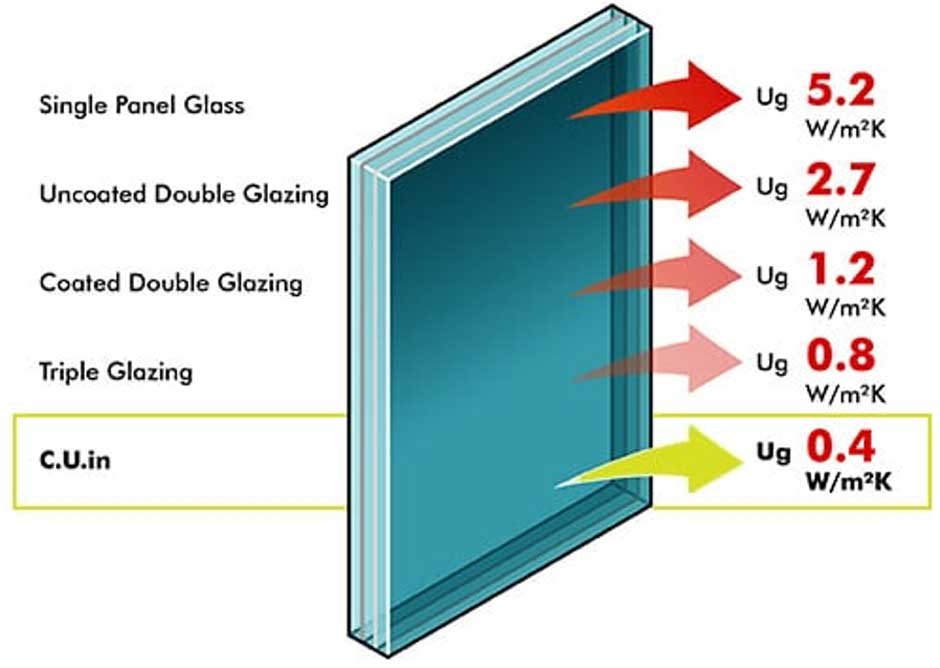
You should use energy-efficient doors and windows in your home to protect your home from excessive heat or cold. You should learn everything, including the benefits, drawbacks, and u-values of each type of glass. The glasses used in them are often classified as single, double, triple glazed, and C.U.in glasses.
- The U-value of single glazing glass is approx. 5.2 W/m2
- The U-value of double glazing glass is approx. 1.6 W/m2
- The U-value of triple glazing glass is approx. 0.8 W/m2
- The U-value of C.U.in glass is approx. 0.4 W/m2K
Single Vs. Double Vs. Triple Glazing Vs. C.U.in
Here is a detailed comparison of
| Single Glazing Glass | Double Glazing Glass | Triple Glazing Glass | C.U.in Glass |
| Most Economical Option | Great Thermal And Acoustic Insulation | High Thermal And Acoustic Insulation | Better Thermal Performance |
| Suitable For Hot And Tropical Climate | Cost-Effective And Energy Efficient | Saves Energy And Reduces Heating Bills | Eco-Friendly & Sustainable (Low Co2 Footprint) |
| Releases Heat Easily | Boost Property Value | Reduced Noise And Sound Transmission | Easy To Install & Energy Efficient |
| No Noise Protection | Hassle-Free Maintenance | Less Cost-Effective | Lower U-Value & High Noise Protection |
Single, Double, Triple, or C.U.in: Which Is Best For Your Home?
There are advantages and disadvantages to each variety of glass. Often people get confused between triple glazed glass and C.U.in glass. When considering both performance and cost, however, C.U.in glasses emerges as the clear frontrunner. It has unrivalled performance for its weight, cost, and longevity. The cherry on top is C.U.in’s stellar reputation for customer support. Visit the website to learn more about the advantages, and get in touch with the C.U.in staff if you have any questions.

